| Courses | ||
| Conabio » Biótica © » About de Biótica » The History of Biótica |
|
The History of Biótica© Due to the vast array of databases that already exist, and the diverse data derived from the projects funded by Conabio, it was felt that it was necessary to develop a unique biological data model. This should be able to hold and manage the variable biological information available, and should be easily consulted. The model developed is called BIÓTICA. The first version was operational in September 1995; it attempted to bring together, synthesise and homogenise taxonomic, biogeographic and geographical information. The database was designed to be used by both the National Information System on Biodiversity (SNIB) and by the individual user. This first version of the model consisted of 39 relational tables and was developed using Microsoft Access® as the basic system for holding data. (see Figure 1). It was used by 8 projects funded by Conabio.
Figure 1. The Biótica Information System©. The main screen of version 1. Due to the quantity of data that needed to be incorporated into the system, the need for a validation process, and comments from many experts who had worked with Conabio on the first version, the model was modified and a completely new format was developed. In May 1996 the second version appeared (see Figure 2) which consisted of 45 tables. This second version was used by about 90 of Conabio’s projects, many of which made changes to the database in line with their specific project requirements. The new version was user-friendlier, and faster and incorporated a validation process. The following list includes some the significant new features:
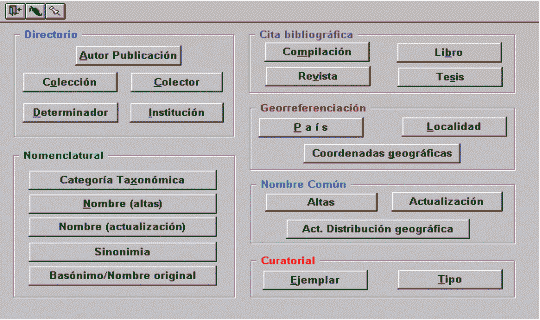 Figure 2. The Biótica Information System©. The main screen of version 2. This second version of the system was basically oriented towards entering data, and providing different ways of generating predetermined reports by user groups external to Conabio. However, when a user wanted to make an unpredefined query, he/she needed experience in a relational database model and in Access®, which complicated the situation, and meant that it was difficult to extract the information. Consequently, the users became experts in BIÓTICA and those working in Systems Development and in the Biótica Inventories Departments of Conabio, were constantly being asked for help with querying and use of the system, as well as how to adapt the system to meet individual needs. This resulted in this version having a large number of options to solve the specific problems of each user. Soon it was obvious that there was a need for a new system, useful to external users. This was vital for the success and maintenance of the National Information System on Biodiversity (SNIB) so that all users continued using the system and updating the data. Therefore, in January 1999 Conabio released version 3.0 (see Figure 3), whose new features were oriented towards the external user and contained 33 tables. Some of its major new features were:
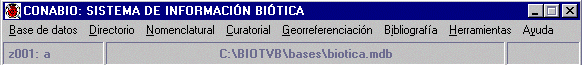
Figure 3. The Biótica Information System©. Main screen of version 3. This version satisfied to the many requests for adaptations of the system by external users with a dynamic system of catalogues, where each user incorporated further data as required. The database also analysed the data in a number of ways using tools which permitted to export and import information to and from certain systems. These tools included predetermined reports (as in version 2). In addition, these dynamic reports allowed users to generate unpredefined queries, without the need for an in-depth knowledge of the data model, with knowledge only of their own data. Also, a system for creating labels was developed with a template for each generic group. The designs of these labels were implemented by Conabio, after receiving examples of the labels the users required. The visualisation of data was also considered and a small GIS module was developed that directly interacted with the
data, so that geographic references for each specimen were be visually represented.
Biotica's version 4.0 was released on Februrary 21st, 2002.This version give us tools that had been improvement from 3.1 version,besides new developments that allow us to shape a new system in where us can capture more diversity of data, with more options for customizer and routines for information's validation. This model is composed of 70 tables. The following diagram shows the main modules of the Biótica © v.4.0 Information System.
At this time Conabio is engaged in generating consultations as well as seeking the possibility of using other managers of databases, for example MS SQL Server. Access®, Visual Basic®
, Excel® by Microsoft Corporation
|
||
|
| Home Page | About Biótica © | Distribution of Biótica version 3.1 | Distribution of Biótica version
4.0 | |